ERP distribution software manages logistics operations and office activities (front and back) of wholesale and distribution companies. This type of software ensures that products sold are delivered promptly and determines product demand. Departments in charge of inventory, logistics, and warehousing are most likely to use the distribution ERP. The distribution ERP offers features to aid with assembling and kitting; distributors sometimes combine products before selling. They also provide modules for sales and purchasing, accounting, and even human resources.
Table of Content:
- What is ERP distribution software?
- The top distribution ERP software for wholesale distribution, financial management, and Storehouse management.
- Features that will solve your business needs
- Benefits for business owners building their company.
- Who uses the Distributor ERP management software.
- What are the alternatives to ERP Distribution Software available?
- Which companies will benefit most?
- How is implementation done?
- Supply network automation and other trends.
- Distribution Software Solutions.
What is ERP Distribution Software?

The Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) distribution provides wholesalers and distributors with solutions for the tasks involved with distributing goods. The management system includes Storehouse management systems, inventory control, marketing, shipping, fleet management, and customer relationship management (CRM). The software provides functionality for all distribution processes by streamlining them utilizing a singular platform.
Distribution business purchases finished products from the manufacturers and sell them to individuals or other companies. Some distribution companies may do the same and sell them to manufacturers. To help these companies, the ERP Software provides a central repository that aids in maintaining better relationships with customers, manages all the processes involved in distribution, and allows the companies to analyze their operation from a financial and performance perspective.
The Top Distribution ERP Software For Wholesale Distribution, Financial Management, And Storehouse Management

There are a few significant examples of the ERP solutions for distribution:
The Cloud – premises ERP
The Cloud ERP is slowly replacing legacy systems delivered on-premises. There are two examples of Cloud ERP solutions for distribution; firstly, traditional – premises software. This modernized software moved to the Cloud—secondly, the Cloud-native products are only available as a subscription model. The Recurrency ERP is a completely cloud-based ERP system. This characteristic grants users access to business information on-the-go, remotely or out in the field.
Industry agnostics
Industry agnostics are also referred to as the vertical-focused ERP. Multiple industries, from manufacturing and retail, to mining and construction, are covered by the wholesale sector. Each industry has needs for special transportation and storage conditioning. For example, chemical distribution requires protection from contact with potentially hazardous materials, while food distribution relies on refrigerated warehouses or modes of transportation. For instance, the Recurrency automated ERP is available for use by any of the above mentioned industries. They have tenants that are both manufacturers and distributors. This is because they have a software that is compatible with any ERP a company may be using, they are truly agnostic.
Standalone
Some ERPs will focus solely on the distribution procedure; however, the standalone ERP for manufacturing also provides features for logistics. Manufacturers who are advances in logistics benefit more from using ERPs such as ETO, ERP, mixed-mode ERP, and discrete ERP.
ERP Features That Will Solve Your Business Needs
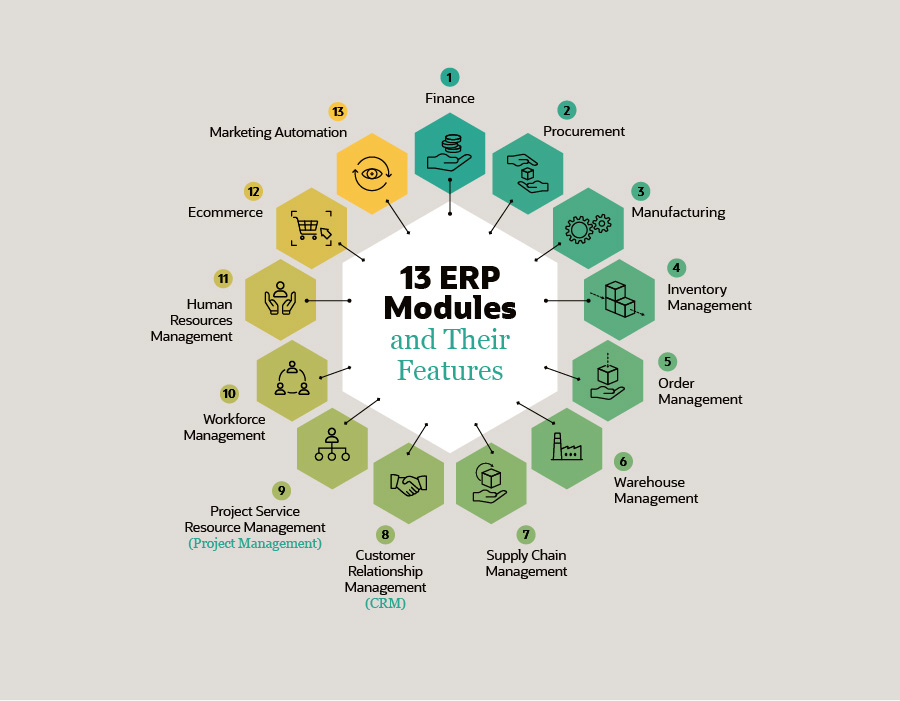
A system dedicated to distribution is built to serve every business service involved in the distribution process. A software feature is created to aid the business in a specific area; thus, owners are advised to always bear their business concerns in the distribution procedure. Distribution ERP systems hence include a wide variety of capabilities and software features. These include:
- Accounting – Financial management features enable businesses to manage their accounts payable, accounts receivable, generals ledgers, and other financial aspects involved in the distribution proceedure. Businesses also have access to features that set different modes of payments on their invoices, ensuring timely payments from their customers. ERPs are also time and cost-effective in the long run. For instance, paying and collecting funds via electronic fund transfers helps you avoid the cost of preparing checks or having to carry deposits to the bank. The information collected from an ERP is also vital in assessing your business’s financial health.
- Inventory – Inventory tracking of finished goods stored in their multiple warehouses across multiple locations is critical for distributors. Distribution ERPs allow inventory managers to monitor the inventory movements in the present to ensure that the company can satisfy the customer’s orders. Using the business intelligence and analytics modules in ERPs is also beneficial. This capability allows business owners to take note of which products have no demand and take action immediately. These items in question could be returned to the supplier or offered to the customers at a reduced price and minimize surplus inventory. It is also critical to future planning. Inventory tracking is one of the demand forecasting features that ERP Softwares such as that of Recurrency offers.
- Warehouse management – These management features allow businesses to manage all aspects of their inventory. This involves inventory optimization features that track the sale orders and match them with inventory availability and decision support system features that allow businesses to identify a stock that has not been purchased. This form of management is another feature that is offered to businesses under demand forecasting, this is also available in the Recurrency ERP.
- Purchasing – Purchase orders are created to satisfy the customer demand; proactive companies use demand forecasting to order goods. This is without having firm orders on the goods from customers. This demand forecasting feature is offered in the Recurrency ERP Software.The ERP helps find and keep the optimal balance between the quantities of goods ordered and customer demand. ERPs also provide Order Administration Systems; this makes it easier for purchases to be tracked through order entry. An order entry ensures a customer’s order is recorded in the business’s handling system. This aids a business to be more critical when decision making and efficiency.
- Sales and marketing – Customer Relations Management Features allow the company to foster a more personal relationship with their customers; hence, most distribution business planning softwares would have them. They provide a comprehensive overview of the customer from; contact information, purchase history, contact activity, and related selling opportunities. This aids in developing more effective customer communication. Some systems even provide customers with a portal through which they can make orders and track the estimated arrival of their goods. The ‘tasks’ that are barebones to-do are not listed.
- Assembly – Manufacturing software is not needed in distribution companies; however, they may require light production. This is also referred to as kitting or assembly. Assembly refers to combining components to create a new product, while kitting brings together products that companies can sell together. Although the operations do not require manufacturing software, they need to be managed to reduce waste and optimize the process.
- Logistics – To be effective, distributors ought to track the movement of merchandise from the suppliers to the customers accurately. ERP provides these functionalities, for instance, picking and packing, receiving, and shipping. Distribution ERPs are tailor-made for warehousing operations.
- Human Resources – HR components of distribution are limited to payroll and workforce management. Capability for talent management is thus delivered via the integration of human capital management systems.
- ECommerce – Some ERP distribution solutions enable users to set up digital storefronts. Distribution solutions such as the Recurrency ERP grants users the ability to integrate with some ECommerce solutions. If a company opts to set up a digital storefront, the platform can be linked to the available inventory to choose from the product catalog. Often included in the software is order management (which is a B2B e-commerce feature).
- Analytics – Analytics dashboards enable businesses to analyze trends and operational data within their business. Users can tailor the dashboard to look at inventory performance, shipment times, and sale opportunities to gather more business intelligence. Users should look out for softwares that has machine learning (ML) and analytics as a critical part of their platform. Having core revenue generating features such as Demand forecasting and Demand pricing while utilizing Artificial Intelligence (AI) and ML. The Recurrency ERP for instance has the above mentioned features.
Benefits Of ERP for Business Owners Building Their Company
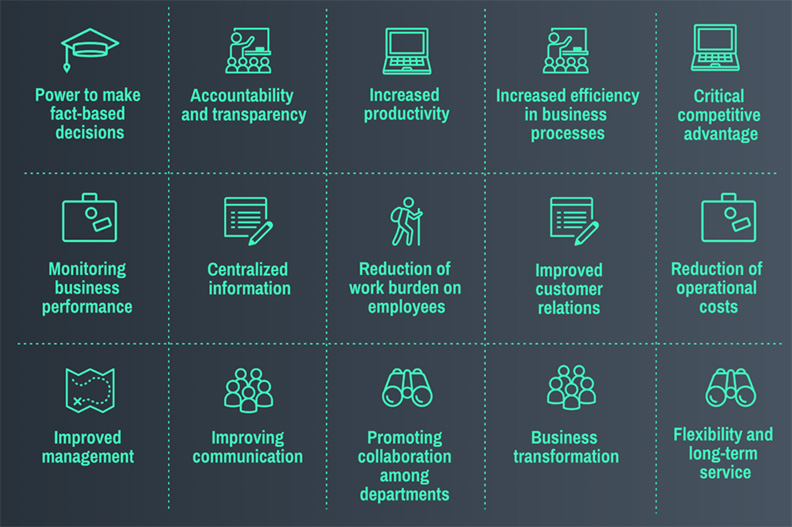
The most common benefits of a distribution software include:
- Single Source of Truth – ERP distribution software services as a centralized business management system that manages all front-end to back-office activities. Wholesale and distribution companies use this system from storehouse management to shipping to a customer, and it helps the companies ensure that their operational and business concerns are streamlined.
- Supply Chain Visibility – One of the critical reasons to install an ERP software system is to achieve unified visibility into all the distribution procedures. The system serves as a unified software that unifies workflows from various business departments. For instance, a retail worker records the sold product into the ERP Software when a retail worker makes a sale. In this case, automatically, the warehouse will be alerted to the inventory levels in that particular store. This lets them know when the stock in that store is running low and when they will need to restock. Businesses benefit from a operating system solution that has demand forecasting features, which aid in the procurement process. Users can determine how much, when, and what to buy.
- Increased Profitability – the distribution software tracks the costs associated with the distribution procedures. These distribution activity costs include shipping and handling, order processing, products costs, and returns. By doing a comparative analysis between these operations costs and the sale numbers, the distributor can calculate the level of Profitability. Businesses are helped to protect their margins by operating system solutions that utilize ML to determine the appropriate rating for each SKU. This is a characteristic of the Dynamic pricing found in an ERP solution.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction – the ERP distribution software makes it easier for the companies to deliver the correct products to the appropriate customer. With the enhanced visibility across the supply network, customers who make an order directly alert the workers at the warehouse to start packing their products. Once orders are packed, fleet managers and customers via live communication can get updates from the drivers on when their goods are expected to arrive. In today’s business world, quick shipping and visibility have become crucial to the customer; hence a company should stay competitive. Users ought to utilize softwares that proactively engage customers by providing them with product recommendations, reorder predictions, and cross sell or upsell opportunities. Procurement utilizes demand forecasting to manage inventory and inform customers of available stock, and have better supply network visibility. These characteristics are an underlying message in all the core features of the Recurrency ERP.
- Sales and Inventory Forecasting – ERP Distribution software makes it easier for companies to plan and prognosticate demand. Using acquisition data and historical sales in the system, distributors and their suppliers can determine which products are high demand or underperforming. This aids with more accurate sales forecasts and helps determine the health of the business.
Who Uses The Distribution ERP Management Software?

The distribution ERP management software is mainly used by departments in charge of purchasing, inventory, logistics, and warehousing. Often these departments are e-business companies, and retail and supply network businesses. The primary users of the distribution software are often the departments involved in logistics; however, the all-encompassing nature of the software allows other departments to benefit from its use. Among these include:
- Procurement: This software is utilized by acquisition professionals to identify and fulfill the demand for raw materials and finished products. The system will determine the optimal supplier of products based on past performance and calculate the quantities required to fulfill customer orders.
- Logistics: The logistics team plans and monitors activities such as picking and packing, inventory receiving, and shipping with the help of the distribution software. Companies can also use the system to outsource some of these operations. Such as shipping and warehousing, and managing their relationships with their partners and suppliers.
- Inventory managers: The ERP software provides inventory management and control, tracks the sales orders and matches them with available inventory, generates inventory count documents for the cycle counts, and includes features to enable the management of warehouses across multiple warehouses. All this visibility makes streamlining easier for packing and shipping. Demand forecasting features in ERP softwares such as those in Recurrency ERP benefit logistics, procurement, and inventory.
The features lacking in logistics/inventory management are available.
- Sales: The sales team would use the software distribution to track the sales quotes, billings, orders. The software also aids in maintaining relationships with customers and prospects. A salesperson can provide the customers with information on product availability or the estimated delivery time by integrating with the inventory component. Sales help track the low-performing products and the number of dissatisfied customers. Users must ensure that they have an ERP Software that has features helpful to the sales team, and that the system is easy to use. For instance, the Recurrency software has a universal search bar that makes everything much easier to find. This is important as it allows field sales to complete their job responsibilities while onsite with a customer, while also making CSR easier.
- Accounting: ERP aids accountants in tracking the sales, costs, and profitability of the company. ERPs such as the Recurrency ERP will aid businesses in these regards. Most of the solutions include complete accounting components, including general ledgers, fund management features, and charts of accounts. The accounting features not available are not listed.
What Are Alternatives To ERP Distribution Software Available?

The alternatives listed below can replace the ERP Software all together or partially:
- ERP Systems: these systems provide functionality for several businesses. These businesses include professional service providers, logistics companies, and manufacturers. A distribution company can utilize the ERP to expand operations in new industry segments not covered by the distribution ERP Solutions.
- Supply Chain Suites: Supply Chain Management (SCM) suites are similar to distribution ERP, with a few notable expectations. The SCM suite does not include components for finance and accounting. They do, however, provide advanced features for logistical operations such as transportation, which are not always present in the ERP Software. Unsure if this is a general comment, or the Recurrency ERP doesn’t run this software often. Instead they utilize MRP for manufacturing companies. Kindly clarify.
Solutions Related ERP Distribution ERP

The related solutions that are mentioned below that can use together with the ERP distribution software are:
- E-commerce platform – ERPs allow a company to set up their e-business stores; however, it is advised that a more robust platform will provide users with a broader range of features. Also, this will enable the linkage of inventory to achieve increased accuracy.
- Sales – The CRM and Sales features such as marketing campaigns and lead generation are not always available in a ERP software. This is why companies often decide to integrate their ERP with marketing automation tools and CRM.
- Accounting – Distribution ERPs can be extremely limited when it comes to fund management features. Thus, it is critical for integration with accounting software to occur. For example, an ERP Software may provide invoicing and cost management capability but doesn’t cover some requirements such as revenue optimization.
- Core HR – As aforementioned, for the sake of severability, integration is required. A distribution ERP may have HR features such as payroll; however, talent management or core HR software is critical. Some businesses choose to have a separate payroll software for specific business concerns like a global payroll.
- Retail POS – A wide range of distribution systems provide a Point of Sale. If the POS is not part of the ERP, users can seamlessly integrate the Software with their ERP Software. When a purchase is made, this automatically updates the inventory in the store and tracks the product’s performance. This is vital if a company hopes to successfully reach all its order fulfillment. Building lasting customer relationships is achieved by proving that your business is reliable and efficient.
Difficulties Involved In The Implementation Of An ERP Distribution Software

A distribution ERP software helps close many visibility gaps across the supply network; however, it has its difficulties. These challenges are present from the implementation time to the cost, and the possible issues can affect the company’s bottom line in the distribution industry.
- Implementation time – ERP Software spun a long implementation time across all departments. This process can take a few months to a couple of years as users shift from old legacy systems that likely had all their distribution data. Thus, it is important to keep in mind these long implementation times and be patient. ERP Softwares such as the Recurrency ERP have an initial integration time of 15 minutes only. Their ramp up period is between 60 -90 days which is significantly faster than any ERP Software in the market.
- Cost – The biggest obstacle that one runs into with any distribution management software is the expense. The average value of an ERP Software ranges in the thousands, and for a small or growing business, this would be a costly sum. The cost of the available ERP Softwares vary, and the cost increases with the number of users of each business planning software. This system is a worthwhile investment as it is meant to be used for five years or more within its technology stack. If your company has the financial means, then this will prove to be an intelligent investment. Primarily this is because this system will cover all business processes rather than creating a need to introduce many disparate solutions. Thus, users are encouraged to research and find ERP Software providers who are transparent about costs incurred. For instance, with Recurrency users are not charged for onboarding, training, implementation, or and any maintenance.
Which Companies Will Benefit Most?

Unlike the Industry-Agnostic ERP software, the ERP distribution software focuses on the business concerns of the following types of companies:
- Wholesalers and distributors – Often when medium or large manufacturers have departments charged with distribution when they do not outsource logistics operations. This department may require its business planning software. It is not atypical for such companies to have different systems for different purposes. In this instance an industry agnostic ERP is a viable solution for any company in these areas, such as Recurrency ERP.
- Retailers – Many of the distribution software provides retail features. These features allow retailers to use the same system for the front office, back office, and in-store activities. These features make it more efficient and quicker for the workers to look up customer part numbers and vendor part numbers. The POS system mentioned above allows for various payment types to ensure customers have their needs met.
- Manufacturers – Often when medium or large manufacturers have departments charged with distribution when they do not outsource logistics operations. This department may need its system. It is not atypical for such companies to have different systems for different purposes.
- Third-party logistics providers (3PL) – These companies manage logistical operations on behalf of their clients. The ERP software allows them to manage the inventory of their clients and track the movement of goods from the supplier to the end-users.
How To Choose The Best ERP Distribution Software

The list of requirements should include essential features needed by the buyer to manage operations. For instance, if a buyer already has a financial management system they don’t plan to replace, they should not include fund management in the list. The following includes what requirements a buyer should bear in mind:
Compare the ERP Distribution Software Product available by doing the following:
- Create a long list that includes the options that may provide the buyers with the capability they need. The long list should consist of both distribution software and systems. If the buyer is a manufacturer, this should include a logistics component.
- Make a shortlist to eliminate products from the long list using criteria, for instance, the software’s delivery model or the vendor’s global presence. Buyers also have the option of eliminating vendors who are unwilling to respond to their RFIs or RFPs (The Requirements gathering for ERP Distribution Software).
- Conduct demos that focus on how each product provides real-time data and supports distribution activities. These activities include warehouse operations and replenishments. It is also critical that you examine how user-friendly the system is; the user experience is vital for regular employees to managers and mobile employees.
The Selection of ERP Distribution Software
Choosing a selection team:
The selection team ought to include managers from every department that would benefit from introducing the software. These departments may include procurement, logistics, warehouse, and inventory management. You can also include other departments that use the system, like sales, HR, and accounting. When dealing with more complex selection projects, you will require dedicated project managers and external consultants who have experience in the field.
Negotiating with your vendors:
Products found on the shortlist are often very similar; thus, it is up to the buyer to negotiate with each vendor to make a final decision. The negotiation process has integral moments, such as the services provided by the vendor and the value of the software.
Reaching your final decision:
When making your final solution, the most critical point is the estimated ROI of the software. The vendors will provide an estimated ROI of the software; hence it is important for buyers to ask for proof that holds them accountable. For instance, a buyer may conduct research and determine how the software in question has aided another company in a similar industry.
The Cost of an ERP Software
The cost of ERP Softwares is often very straightforward; it, however, advises that buyers look out for any hidden costs. For example, remember that the ERP software may include the electronic data interchange (EDI), but it requires arrangement for different trading partners. If you plan on expanding your business, it is important to find out how much it will cost to accommodate new users or implement the system in a new location.
Return on Investment (ROI) – The user can compare the ROI mentioned above with the actual benefits of the software, such as an increase in sale volumes or cost reductions.
How Is Implementation Done?
| How is the ERP Software Implemented? |
|
| To whom does the responsibility for the Implementation of the ERP Software lay? |
|
| What does the implementation process entail when you are dealing with ERP Software? |
|
| When is the best time to implement an ERP distribution software? |
|
Supply Network Automation And Other Trends
Significant trends can be observed in the distribution market; these include increased visibility and more automation across the supply network. Other trends that may emerge in the foreseeable future include
Omnichannel retail
This growing trend enables customers to shop and return items via various retail channels. For instance, a customer can purchase a product online and return it to a physical storefront if they are discontented with the products. For a business, employees must keep bar codes, and item numbers track for accountability.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT technology further aids warehouses and businesses in maintaining the visibility of their inventory. For instance, a business attaches radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags to essential or higher-priced products, which provides businesses with visibility of the products until they are bought. These tags also provided the customer with knowledge on where the product is, which helps deliver ETAs and notifications on any delays.

Distribution Software Solutions
Some Solution providers include:
- Oracle NetSuite – NetSuite is a Cloud computing company that caters services to manage business customer relations, operations, and finances. The company was started in 1998 and offered a web-hosted accounting operating system. Currently, NetSuite offers modular products, and the cost of a subscription is not fixed. The cost all depends on the modules selected and the size of the company. The platform provided is accessed through the Cloud and is tailored for small and medium-sized businesses.
- SAP ERP – This Enterprise Resource Planning ERP Software incorporates the key business activities of a venture. It was developed by the German company SAP SE. It was developed on the SAP 3 software, which The company developed in 1992. The ERP Central Component eventually replaced this version. This new system merged SAP Business Warehouse, Internet Transaction Server, and Strategic Enterprise Management. This allowed users to utilize them under one instance.
- XTuple – XTuple is open-source software that provides inventory and financing management tools. It is an enterprise software company that has developed and markets software. XTuple began developing under the name of OpenMFG in the year 2001. They had a commercially licensed ERP that was geared towards small and mid-sized manufacturers. The company has adopted a ”community code”, which means that customers can view and modify the source code. This source code is, however, not publicly available, unlike an open-source software would be.
- Ddi system – Developed for wholesalers to streamline inventory, financial management, and performance analytics. The company has productivity boosters such as; Strategic Partners, Mobile Solutions, Content Integration, Multi-Channel Commerce, Wireless Warehouses, ECommerce Pro, and Card Processing Services.
- Acumatica – A technology provider that develops Cloud and browser-based ERPs. The software provided by Acumatica is geared towards small and medium-sized businesses. The software can be run from a data center, deployed on-premises, or run from a Cloud computing platform. Automatica’s ERP applications are built on its internally developed platform. The software can be subscribed or licensed to as a SaaS (Software as a Service).
- SAP S/4 HANA – This ERP is designed to cater to large enterprises. The ERP integrates lines of business capabilities with industry solutions, and applications such as Business Suite and ERP can run on this database. It was created to cover the day-to-day activities of a venture. These include order-to-cash, procure-to-cash, request-to-service, and plan-to-product.
- Infor LN – The company produces cloud software products for companies in industry-specific markets. Infor LN is specifically designed to fulfill the business concerns of the manufacturer. The Industries that the company caters to includes: Manufacturing, Defence, Hospitality, Healthcare, Service Industries, Public Sector, Distribution, Energy & Natural Resources, and consumers.
- Brightpearl – This cloud-based ERP is developed for wholesalers and retailers of all sizes whose goal is to mechanize the back office. The solution provided enables omnichannel businesses to manage their ventures from a single system. This would aid you in aligning your online and offline sales along with any other processes. Since it is built on merchants, the company has an understanding of the different trading models, be it; marketplace, online, offline, or retail. It offers back-office solutions such as inventory and sales order management, purchasing and supplier management, financial management, and logistics. Additionally, it enables the integration of major e-business platforms and online marketplaces.
- Dynamics NAV – The Microsoft Dynamics NAV is an app part of the Microsoft Dynamics Family. The app assists small and midsize businesses with electronic commerce, supply networks, finance, customer relationship management, and manufacturing. It can also be utilized by local subsidiaries of international groups. It is composed of three major parts: the Database Server, the application server, and the client or the user of the software.
- ePROMIS SAP – The ePROMIS was developed with larger companies in mind, and the solution focuses on streamlining and synchronization. The enterprise functionalities tackled by the ePROMIS enterprise are finance, assets, human resources, customer relations, analytics, and planning. They have a system that can be customized to the nature and organizational structure of the company. The components of the ePROMIS business planning software are; Sales Management, acquisitionManagement, Human Capital Management, Asset Management, Fleet Management, and Financial Management.
- SAP ByD is a comprehensive sold and operated as a service (saas) ERP. It is serviceable for small to medium-sized ventures, as well as subsidiary businesses. The principles of Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) are what this software is built on. Business capabilities are integrated through messages. The software is designed for business processes from human resources to financials with embedded support, business analytics, mobility, and e-learning.
- Epicor Prophet 21 – Epicor Prophet 21 is a cloud-based solution designed to cater to the needs of businesses. The company offers several industry productivity solutions; ERP for distribution, ERP for building supply, automotive, retail, and manufacturing.
- Magaya Supply Chain – Magaya offers supply network software or logistics software. The suite of applications offered is designed to manage, optimize, and automate supply network operations. Often this will include inventory management, supply network analytics & visibility, and warehouse operations. The Cloud fully supports the Magaya solution; hence, it is available on a subscription-based license.
- Skubana – Skubana offers a cloud-based ERP Software that is utilized in handling and automating inventory, analytics, purchase orders, order operation, and accounting.
- Epicor BisTrack – The BisTrack is a management software designed to cater to lumber and building materials businesses.
- Infor Distribution SX.E – This software was developed specifically to cater to the needs of the wholesale distribution industry.
- Infor M3 – This is a Cloud-based distribution and manufacturing system.
- OfficeBooks – This is a web-based business management application geared towards distributors and manufacturers. OfficeBooks has an automated system.
- BizAutomation – The BizAutomation Cloud ERP Software was designed specifically for small to midsized businesses. It provides a suite of management software applications. They serve the following industries: manufacturing, service industry, and retail.
- Epicor Eclipse – It is also called the Eclipse Distribution Management System or Intuit Eclipse DMS or Activant Eclipse. The Eclipse software is real-time accounting software. Wholesale businesses utilize it in the PVF, Plumbing, and Electrical industries.
- OpenPro ERP – OpenPro is involved in developing licensed Enterprise Resource Planning software using open source LAMP technology. The company was founded in 1998 and had a variety of customers across several industries.
- Encompass – Encompass provides a beverage distribution software that is Cloud-based and a Software as a Subscription. This solution is designed to meet the needs of make-to-order and mixed-mode manufacturing companies.
- Sage 500 – Sage offers a complete enterprise management solution. The company offers customized solutions to fit your business concerns and organizational structure.
- Cavallo – The Cavallo ERP system is developed for distributors. Development commenced in 2003 when the founder of Cavallo expressed frustration with the Microsoft Dynamics GP as a distribution management tool.
- Deskera Books – Deskera is Cloud-based accounting software that aims to help small businesses run. It was founded in 2008 with the idea that small businesses needed a hand to grow. This is vital as small businesses are the backbone of society.
- VIENNA Advantage – VIENNA Advantage has been implementing ERPs since the year 2005. They are dedicated to an open-source model that involves the community and allows for product expansion. They offer their services to companies across many industries, including Telecom, Distribution, Public Sector, Discrete Manufacturing, Construction & Real Estate, Life Insurance, Oil & Energy, Textile & Apparels, Retail & supply network, Food & Beverage, ECommerce, and Education among others.
- ERP-ONE – The ERP ONE software is specifically designed to cater to midsized to large wholesalers and distributors. The Cloud and On-Premise ERP includes all the features needed by a distributor to mechanize their processes.
- OMS (Office Master System) – The OMS is an inventory optimization with an integrated accounting application. It integrates the wholesaler’s back-office through the internet with the business-to-business and the ECommerce.
The table below outlines the features that the aforementioned ERPs have to offer to their users.
| Operating system: | Features: |
| Oracle | The Oracle Netsuite ERP supports Customer Interaction Management, Professional Services Automation (PSA), E-commerce, Human Resource Management, Tax Calculation, accounting, billing, management reporting, payroll accounting, sales tools, analytics, and catalogue management. |
| SAP ERP | This ERP is made of the following business modules; Project Systems (PS), Controlling (CO), Financial Accounting (FA), Human Resources (HR), Storehouse management, Sales & Distribution (SD), Asset Accounting (AA), and Plant Maintenance (PM).
The latest version enables the following business operations; Financial supply network Management, Human Capacity Management, Corporate Services, and Operations, among others. |
| XTuple | XTuple ERP has the following features: Human Resources, Financials, Manufacturing Management, Purchasing Management, Sales Management, Quality Management, Product Technology, and catalogue management. |
| ddi System | DDI System has the following core features; embedded CRM, Financial management, catalogue management, Order fulfillment, Analytics & Reporting, Point of Sale, Strategic rating, Warehouse Logistics, Shared Calendars, and Paperless workflows. |
| Acumatica Cloud ERP | Acumatica has the following features to offer: Payroll, Manufacturing, Project Accounting, Field Service, Retail eCommerce, Financial Management, Customer Interaction Management, Construction, Distribution, Process Manufacturing, and Extended Accounting. |
| SAP S/4 HANA – Intelligent ERP System | The S / 4 HANA system has the following features: Product Life Cycle Management (PLM), Investment Management (IM), Controlling (CO), Human Capital Management (HCM), Plant Maintenance (PM), Production Planning (PP), Project Systems (PS), Sales & Distributions (SD), Strategic Enterprise Management (SEM), Logistics Information Systems (LIS), Logistics Management, Industry Solutions, Treasury, Materials Management (MM), Customer Service (CS), Enterprise Performance Management (EPM), Environment, Health & Safety (EHS), and NetWeaver.
The software also integrates the above capabilities with; SAP SRM, SCM, and CRM. |
| Infor LN | The LN ERP has the following features: Performance Management, decision support system, Risk & Compliance, Enterprise Asset Management, Advanced Insights, Visibility & Control, Warehousing & Transportation, Human Resources, Workforce Management, Field Service, ECommerce, Planning & prognosticate, Global Trade & Finance, Product Lifecycle, Talent Management, Workforce Management, Industry ERP, and Licensing, Permitting & Billing. |
| Brightpearl | Brightpearl provides the following features: Retail Management, catalogue management, Warehouse & Fulfillment, Purchase Order & Supplier Management, Sales Order Management, and Customer Management & Marketing. |
| Dynamics NAV | The Dynamics NAV provides support for; Logistics Management, Distribution, Customer Interaction Management, Human Resource Management (HRM), Service Management, Sales & Marketing (SM), Project Management (PM), Resource Management (RM), Storehouse Management, Financial Management (FM), and Manufacturing. |
| ePROMIS | The ePROMIS has the following features: Cloud, Hybrid or Web based solution, decision support system, Document Attachment System, Fully developed and integrated ERP Architecture, and Electronic Approval System. |
| SAP ByD (SAP Business By Design) | The software is designed to provide business operations such as; Compliance Management, Financial Management, Project Management, Customer Interaction Management, Supplier Relationship Management (SRM), Executive Support & Compliance Management, Professional Service Automation (PSA), Business Analytics, Fund & Grant Management, Human Resource Management, and Business Analytics. |
| Epicor Prophet 21 | Prophet 21 focuses on the following business operations: Customer Experience, Sales Management, ECommerce, Value added Services, Inventory & supply network, Product Management, Production Management, Finance & Accounting, decision support system, and Storehouse management. |
| Magaya Supply Network | The Magaya offers: Logistics Management, Storehouse management, and Purchase Order Operation. |
| Skubana | Skubana offers: ECommerce, catalogue management, and Order Operation. |
| Epicor BisTrack | The BisTrack offers: ECommerce, Analytics & Reporting, Inventory & Warehouse, Technology, Customer Management, Sales Management, Financial Management, Mobility, Delivery Dispatch, and Value-added Services. |
| Infor Distribution SX.E | The Distribution SX.E offers the following business features to wholesale businesses: catalogue management, Value added services, Omnichannel Engagement, Storehouse management, Financial Management, and Sales Management. |
| Infor M3 ERP | The M3 ERP offers the following business operations; Production Planning, prognosticate, Demand Planning, Value added Services, catalogue management, Workflow Management, Mobile Enablement, Analytics, Equipment Configuration, and Logistics. |
| OfficeBooks | OfficeBooks ERP offers the following business operations; Contacts, Work Orders, inventory optimization, Purchasing Management, and Sales Order Management. |
| BizAutomation | The BizAutomation provides the following features: Order Operation, Financials, Human Resource Management, Manufacturing, Procurement, CRM, Professional Services, Omnichannel ERP, Inventory, Business Portal, Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), Analytics, and Automation. |
| Epicor Eclipse | The Eclipse software offers the following supports to your business; System – wide Business Management, Logistics Management, Supplier Relationship Management, Demand Management, International Trade Logistics, Warehouse Management System (WMS), Transportation Management, Distribution Process Management, Retail & Commerce, Human Resources, Product Technology, and Financial Management. |
| OpenPro ERP | The OpenPro ERP Software offers the following: Storehouse management, inventory optimization, Sales Order Processing, Purchasing, Customer Interaction Management, Information Management System, Document Imaging, Workflow Management, Payroll Human Resource System, Fixed Assets, and Credit Card Processing. |
| Encompass | The Encompass Software provides support in the following areas: Job Management, Order & Quote Management, Field Service, Data Collection, Product Lifecycle Management, Supplier Relationship Management, Product Configuration, Currency Management, Multi-site Management, and E-business capabilities. |
| Sage 500 | The Sage 500 solution offers support through the following business operations: Time Management, Project Management, Order Entry & Purchasing, decision support system, Accounting & Finance, Manufacturing, eBusiness Suite, and HR Management & Payroll Processing. |
| Cavallo | Cavallo offers the following operations to its users: Customer Management, Automated Workflows, Order Entry, Mechanized Alerts, Personalized Dashboards, Universally Accessible, Quick Payment, Customer Data, and catalogue management. |
| Deskera Books | Deskera offers small businesses with the following support: Customer Support, Mechanized Statement Generation, Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, General Ledger, Product Management, Finance Management, Revenue Recognition, Budgeting, Order Operation, Order Fulfillment, Advanced Financial Reports, Procure-to-pay Process, Multi-Currency, Out of box Reports, and Statutory Compliance Management. |
| VIENNA Advantage | VIENNA Advantage offers the following to its users: decision support system, Document Management, Financial Management, and Human Resources & Payroll, Enterprise Asset Management. |
| ERP ONE | ERP ONE Distribution Software provides its users with the following features: Quality Control, Sales Order Entry, Sales Analysis, Contract Rating & Item Sales, Cash Management & Accounts Payable, Tab & Billing, Cach Management, Accounts Receivable, General Ledger, Customer Relationship Management, Kitting, Assembly, catalogue management, Storehouse management, Inventory Replenishment, Shipping & Distribution, Wireless Warehouse, Document Management, Data Analytics, Electronic Data Interchange, Document Management, and Interactive Management Reporting. |
| Office Master System | OMS offers its users the following: Billing & Invoicing, Analytics, prognosticate, Import/Export Management, catalogue management, Customer Management, Picking & Routing, Barcoding, Inventory Tracking, Item Management, Lot Tracking, Manufacturing catalogue management, Inventory Optimization, Supplier Management, Serial Number Tracking, Shipping Management, Materials Management, Mobile Access, Order Operation, Returns Management, Production Management, and Cost Management. |