What are ERP and its types?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software is a suite of applications that manage core business processes. For instance, accounting, human resources, customer support, purchasing, sales, CRM, and inventory. This system is integrated as opposed to individual software, which is designed for singular business processes. There has been increased traction among businesses, both big and small, that ERP solution software’s have gained. This is owing to its centralized approach to business processes, and this enables you to collect, manage, store, and interpret data from varying business units. ERP is also utilized to streamline the cross-departmental workflows and automate back-office processes. Despite the utilities mentioned above that ERPs serve a company, there are still businesses that have not been implemented.
Table of Content:
- Examples of ERP Softwares in the market.
- Why should you use ERP Software?
- Types of ERP Systems.
- What modules are found in an ERP Solution?
- What factors to bear in mind while choosing the right ERP for you?
- The Cost of ERP Software in the market.
- Potential challenges that you may face with ERP Software.
- The Latest ERP Trends.
- What to do to maximize your ERP Software.
Examples of ERP Software in the market

To better understand what an ERP tool is, below are some of the software solutions on the market. These platforms have comprehensive features set, scalability, easily configurable systems, and integrated interfaces.
| Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software Solution: | Description: |
| NetSuite | The NetSuite Integrated ERP software is designed for fast-growing companies. Thus it offers a scalable interface equipped with financial management and inventory management to vendor management and payment processing. It has the capability of automating a wide range of front and back-office to streamline operations simply. It also provides you with robust reporting tools which offer actionable insights into your performance. |
| Tiplati | This is the billing and invoicing software. The Tiplati ERP allows a company to focus on its growth and improve its business by providing tools to move past ordinary transaction finance. This is done by combining powerful accounts payable (AP) automation tools with global mass payments capability. The software solution has end-to-end enterprise-grade ERP modules, including managing procurement, financial protection, suppliers, and invoices. There are also smart real-time payment reconciliation features that are fitted with tools for tax and VAT compliance. |
| Rossum | Rossum is a web-based account payable software. This software provides organizations with a document management-based automation and workspace utilized for business process management. Data such as invoices and other forms are automatically scanned, collected, and validated through self-learning Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology. It is possible to deploy the aforementioned unique document management technology in many enterprise-use cases, including task management and AP automation to logistics and compliance. Also, it integrates with other business systems and has a robust analytics and reporting module to boot. |
| Score | The score is a cloud-based business management software. It is a powerful solution designed for professional services businesses, primarily those in the consulting, advertising industries, and IT. The cloud platform provides robust tools, such as tracking and scheduling, project management, quote management, CRM, financial management, reporting, and customization. Businesses leverage the tools for team time usage and plan projects, build client relationships, send invoices, and monitor results into one integrated system. |
| Odoo | The ERP software Odoo is unique due to its open-source modular architecture. The software makes available best-in-class sales and project management functionalities to start. You can choose to extend platform capabilities as your business grows by picking from their extensive selection of ERP applications. These include accounting, eCommerce, POS, Materials Requirements Planning (MRP), and other business processes. The system is also capable of seamlessly integrating with third-party applications allowing you to use your existing systems. |
| Sage Intacct | Sage Intacct is a cloud accounting software designed for small and medium businesses. The platform features ERP capabilities that are made possible via integration, for example, wholesale distribution, retail management, and financial management. It also has workflow management options that allow you to perform bank reconciliation, trial balance, and automated journal entries. It is also very user-friendly, with a no-fuss interface that novice or professional users can get the hang of in no time. |
| SYSPRO | SYSPRO ERP Software is designed specifically for companies in the manufacturing industry. It provides robust tools for accounting, document planning, work order management, and project management. Also, inventory control to easily keep all data and manage all processes from one platform. It is also known for its utilization of BOT agents in charge of automating redundant processes. While also giving you fast support for all aspects of your operations. |
| Oracle ERP Cloud | Oracle ERP Cloud is a business management platform. The platform is an end-to-end solution that provides users with an integrated system for large businesses. These are usually ranging from telecommunication and sales firms to pharmaceutical and manufacturing companies. The ERP Cloud comes with financial planning softwares feature, risk management tools, project execution capabilities, and compliance monitoring options. Additionally, Oracle ERP Cloud offers users a performance management module to help both gauge productivity within your enterprise and also pinpoint how to improve overall operations. |
| Microsoft Dynamics GP | Microsoft Dynamics GP is a business management platform that offers a robust set of features that tackle financial management, human resources management, supply chain management, and workspace collaboration. It is also known for its business intelligence feature that lets users get actionable insights on their ERP data. This platform is also seamlessly integrated with third-party partners, both cloud-hosted and on-premise. |
| SAP ERP | Software ERP providers, SAP ERP, design the SAP ERP Software. This platform comes with customer relationship management and supply chain management functionalities, and it can also be integrated with various applications and modules for other business processes. The software can be deployed on-premise, on the cloud, or as a hybrid model as per your convenience. |
Why should you use ERP Software?

Now that we have examined what Enterprise Resource Planning ERP software is, it is important to consider why you should be using ERP Software for your business activities? The following are the benefits of ERP Software Solutions?
- ERP Software promotes collaboration. It breaks down the walls that can spring up between departments. Data silos are integrated, while a process superhighway links local workstations together. The setup mentioned allows teams that used to operate in isolation from each other to easily come together with other teams inside the ERP platform. SaaS (Software as a Service) ERP also extends collaboration between remote teams and those at headquarters via the internet. This culture of collaboration drives innovation and team play while making businesses more competitive.
- ERP Software increases efficiency within a business. Business functions including; accounting, sales, marketing, production, and inventory are integrated into a singular ERP platform. Thus, it’s easier to collect and access data across the organization, streamlining cross-departmental workflows. Likewise, day-to-day tasks are automated, for example entering data or generating reports. Teams are free to focus on their core deliverables because repetitive manual processes are eliminated. For example, without bugging tech marketing can run a daily web traffic report; or, without chasing the sales director accounting can instantly access the week’s sales stats. Managers and key stakeholders are provided with quick look-ups. At the same time, dashboards allow decision-makers to examine key performance indicators because if they want to investigate more, managers have further access to drill down into details with just a few clicks.
- Data security is increased when a company utilizes ERP Software. Firewalls and restriction control secure ERP solutions to guard against data breaches. Having one data warehouse means that the access points are tightly monitored, and security is concentrated. Also, user permission rules give the admins the flexibility to lock in sensitive data without limiting user access to other relevant information. Terminated employees’ access can be quickly deactivated by administration and grant permission to new ones. User activities are also displayed, so you can easily spot unauthorized actions or suspicious activity patterns in the system.

- It aids a company in complying with industry regulations. Most ERP solutions have built-in regulatory process standards as well as compliance reporting. This is to help businesses meet myriad business requirements. ERP solutions also subscribe to reporting protocols for financial accounting, product regulations, and data security.
- Equips you to make accurate forecasts. Forecasts shape strategies that your business will utilize. Thus, it’s vital organizations get the real picture. ERP lends to a company’s standardized process, disparate business solutions and ultimately enhances data integrity by using a centralized database. Data is sifted for inconsistencies by ERP reporting tools which use advanced filters and analytics. Features of ERP software such as deduplication also ensure data is constantly updated and duplicate-free. Data integrity being intact allows managers to generate reports that result in credible forecasts. Similarly, the estimates are within a sensible range of outcomes. Machine learning and predictive algorithms are used by advanced ERP solutions with business intelligence tools that allow users to look deeper into big data. Companies with a complex data source can leverage ERP for any hidden insights and gain a competitive edge.
- The operational costs of the business are reduced. When key metrics are closely monitored and processes are streamlined, disruptions, delays, and breakdowns are anticipated, and their impact is better handled. This is key in manufacturing and distribution, which are especially vulnerable to disruption. Operating costs are also kept within budget, with ERP allowing production, engineering, customer service, and other business units to work together. Also, using real-time data leads to resolving sudden problems faster. Additionally, ERP software providers often deal with technical problems. Such as patches, give regular updates, and troubleshooting. Meaning you don’t have to factor in maintenance costs in your operational costs.
- Your business will experience operational flexibility. It helps you develop a more streamlined workflow by integrating existing apps into your system or exporting your ERP data to other business apps. Also, systems give you the option to add more modules as your business grows. This is so that you no longer need to replace your system with new software. SaaS ERP gives you mobility because the software can often be accessed on any device so long as there is the internet.
Types of ERP Systems

It is important to understand that the fluidity of ERP dynamics and the diversity of factors affecting it make it difficult to classify ERPs. Thus, an ERP can be grouped either by functional levels, business size, or deployment. To simplify the types, ERP Enterprise Resource Planning System can be grouped as follows:
-
- Generalist ERP. Many legacies and cloud ERP solutions available are generalists. Their adaptation to processes across industries characterizes them. These generalist solutions have strong customization and integration. This is to match varying industry requirements. It’s also not shocking given its large market generalist ERP vendors are also one of the largest in the market. One example of this type of ERP solution software is Oracle NetSuite ERP.
- Open-Source ERP. These ERP solutions are still a tiny fraction of the total ERP market. However, solutions such as Odoo ERP lend to companies with resident tech teams flexibility to develop and integrate their apps into the (ERP) Enterprise Resource Planning Software. For developers, open-source increases the efficiency in usability and user adoption. This is because the ERP can churn out highly customized processes.
- Vertical ERP. They are industry-specific ERPs. Usually, vertical ERP vendors are startups or smaller companies that focus on a niche business area. These include; construction, supermarket distribution, or retail fashion. Among the examples of this type of platform is Microsoft Dynamics AX.
- Small business ERP. They are off-the-shelf cloud or on-premise ERP solutions. Usually, in this type of ERP software system, the ERP is modularized with pared-down features. Small business ERPs like PeopleSoft serve few business processes and leave out the others instead of delivering a fully integrated system. For example, HRM and accounting functions only are featured, with add-on options for CRM, inventory, or supply chain management. They are also known as lightweight ERP.
What modules are found in an ERP Solution?
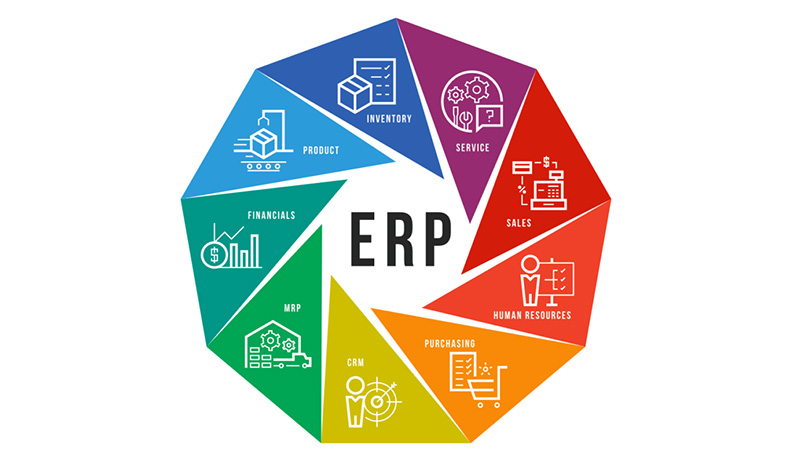
An ERP Solution can either be fully integrated or customized for specific processes. Typically an ERP System will cover the key business processes and have the following modules:
-
- HRM. The HRM module has the standard HRMS tools such as time tracker, timesheet, and database for employee records, job profiles, and skills matrix. HRM modules sometimes also feature performance reviews and payroll systems. The latter of which is closely integrated with the financial management module. This is to manage wages, travel expenses, and reimbursements. Some ERP solutions also have a training or LMS function under HRM.
- Financial Management. The FM module manages your capital inflow and outflow. It also covers standard accounting and finance transactions. These include; expenditures, general ledger, balance sheet, bank reconciliation, tax management, and payments. The module also generates financial reports for different departments and business units.
- Sales & Marketing. This module handles sales workflows such as sales inquiries, quotations, sales orders, and sales invoices. More advanced ERP will also feature taxation rules and a shipping tracker. The Sales and Customer Relationships Management modules work together to earn more profits and speed up the sales cycle.
- CRM (Customer Relationships Management). This module helps a business boost customer service and, eventually, profit per capita. Customer relationships management CRM manages leads, opportunities, and customer issues. Also, it provides a 360-degree profile of your customers. This is done by consolidating their social media activities, purchase history, and past interactions with support reps.
- Manufacturing. Sometimes it is also called engineering or production. This module aids businesses in making manufacturing more efficient in areas like product planning, materials sourcing, daily production monitoring, and product forecasting. Its key functionalities are the bill of material, production scheduling, shop floor control, and distribution planning. In areas such as product planning and inventory control, this module is tightly integrated with SCM and inventory modules.
- SCM. The SCM module covers key aspects of your supply chain, including purchase order management. It also manages product flow from production to consumer and, occasionally, vice-versa for returns or recalls. A key feature of this module is process automation, which streamlines your entire supply chain and makes it adaptive to sudden market shifts.
- Inventory. The material management module, also referred to as this module, helps you measure stock targets, standardize replenishments, and other inventory goals. It utilizes product serial numbers to track and locate items in your company. The inventory module is closely integrated with the Purchase module.
- Purchasing. The purchasing module manages the processes involved in materials procurement. Such as supplier listings, quotation requests and analysis, purchase orders, Good Receipt Notes, and stock updates. Thus it functions closely with SCM or Inventory modules.
Other than these basic functions, there are more advanced ERP platforms, and these also include business intelligence, assets management, and eCommerce. Moreover, an ERP Solution can be vertical with industry-specific features for retail, healthcare, government, and nonprofits, among others.
What factors to bear in mind while choosing the right ERP for you?

Once you have weighed the cost-benefit ratio of getting an ERP and you’re convinced it’ll drive overall profitability for your business. You now need to analyze these key factors to ensure you optimize your ROI.
- Does your organization require an upgrade or replacement of the ERP system? It is important that you first evaluate if you need to get a new ERP system or just an upgrade. The majority of the ERP solutions available today are modularized. Meaning you can simply integrate a module, for example, payroll, with your current applications. This way, you have the lowest possible amount of disruption and costs. However, if your ERP system is ten years or older, it is advisable to replace it. Today’s ERP solutions can be leveraged for mobility, integration, scalability, and deployment options. Also, machine learning, predictive analysis, and advanced reporting are pushing ERP to the next level.
- Consider the amount of training and setup that your staff will have to undergo. If you are considering installing an on-premise ERP solution, you must remember that they need to be installed by someone with technical know-how. If you don’t have an in-house tech team, ensure you understand your service level agreement (SLA). Often, installation is charged separately from the license. Some vendors offer all-in bundled plans. When choosing SaaS ERP, setup is simple, and you just activate an account to access the vendor’s server. On the other hand, ERP is more complex than most business solutions, so it requires user training. You must ensure whether your vendor provides this service. Whether it is bundled in or exclusive to the plan you are considering. Also, the kind of training you’ll receive should suffice for average users to adopt the system, meaning it is easy to understand.
- Go beyond spreadsheets and PDF exports. ERP solutions available today feature advanced reporting. This feature can generate compliant financial statements based on the region you are in. The latest ERP reporting tools also give users in-system queries and smart filters, coupled with real-time data. Users are also advised to look for agile and ad hoc reporting to quickly adjust to evolving business needs and disruptions. Dashboards, conversely, should let you mash up quantitative vs. qualitative data at user, role, and department levels. Identify an ERP software with a standard dashboard function of displaying KPIs with drill-down links.
- The integration capability of your ERP Software is vital. ERP ought to work seamlessly with your current business applications. From top to bottom, there are several integration points you need to consider. Among them are; system-to-system (such as ERP to your existing CRM or HRMS), module-to-system (such as ERP payroll to your current HRMS), and file transfer capabilities (such as exporting/importing PDF, JPG, DOC, CSV files). An ERP with flexible integration is capable of; working with existing infrastructure, expanding its functionalities or, replacing it while ensuring smooth records and filing migration.
- How customizable is the ERP? Other than ensuring the ERP processes match your key business workflows, closely examine your departments. Each department may have different priorities and cultures, which may be contradictory. For instance, accounting saves, while marketing spends, or production lives by daily output, while sales live by monthly quota. A one-size solution won’t fit these myriad workflows. Identify an ERP solution with customization tools, localized dashboards, and configurable workflows, among others. It should allow departments to define their goals and set the ERP based on their parameters.
The Cost of ERP Software in the market
A majority of ERP solutions are priced by quotation for the customized features included. The cost of ERP software is often based on factors such as; having several users, modules, installation, add-ons, maintenance, and training. Let’s look at the pricing models of some of the ERP solutions on the market today.
| ERP Software: | Cost: |
| NetSuite ERP | The NetSuite ERP offers are available by quote. They are priced based on the number of modules you request for your system, the number of users per month, and the kind of add-ons you require. |
| Tiplati | They are similarly offered in quote-based plans because it is deployed according to your specific needs. At times the vendor offers a free trial period. This allows users to know the right mix of features that can help them reach their goals. |
| Rossum | Rossum, just like the ERP vendors above, also offers quote-based plans, and this is because it is rolled out customized to your company’s needs. |
| Scoro | The Scoro pricing plan is based on the number of users and the features. The four pricing plans offered by the vendor include; Essentials which is $26 per user per month. Sales Hub is $37 per user per month. Work Hub is $3 per user per month. Finally, Business Hub is $61 per user per month. |
| Sage Intacct | Like other ERP platforms, Sage Intacct only offers quote-based plans, so you must ensure to contact the vector to get a customized package for your business needs. |
| SYSPRO | SYSPRO makes prices only available by quote. The plans offered are mostly calculated according to your preferred deployment option, the modules you need, and the number of users you want on the software. |
| Odoo | Odoo offers a flat rate of 10 Euros per month, making it comparatively affordable among the options on this table. The fee includes the basic functionalities of the program, and however, separate charges apply for the applications in the system. |
| Oracle ERP Cloud | This cloud ERP has three enterprise pricing structures. They are bundled according to the functionalities needed. The plans available are; advanced financial control plan, a financing reporting plan, and an advanced access control plan. Respectively they cost; $80 per user for each month, $175 per user for each month, and $150 per user. |
| Microsoft Dynamics GP | This vendor offers various pricing plans depending on the preferred licensing. If you want to subscribe to a service, they have a $214 per user package for a month. There is also a hosting plan that costs $134 per user for a month. The perpetual licensing plan is available by quote. |
| SAP ERP | The SAP ERP is only available on a price quote basis. The plans are often bundles depending on the type of modules preferred. Your required deployment option also factors in. |
Potential challenges that you may face with ERP Software

- There is no one-size-fits-all ERP solution. Off-the-shelf or plug-and-play ERP solutions work well with small businesses with straightforward processes. However, for large corporations with subsidiaries in different locations, a uniform system quickly runs into obstacles in a diverse environment. Differences in factors like culture, policies, and regulations make it challenging to implement an overarching infrastructure. The result of this is either the ERP suffers from a low user adoption, or an expensive system is justify unused in a company warehouse. A majority of large enterprises today are adopting a two-tier ERP approach to manage their organizational complexities. Meaning a corporate ERP is used by headquarters, while the subsidiaries use another ERP system.
- Existing applications that are used by your business are unsupported. If your business is currently using a dozen or more productivity apps, then introducing a plug-and-play ERP won’t be that smooth. The more applications you have in place that are actively in use, the narrower your options are to find a fully integrated quick-install ERP solution that will fit your business. If you don’t plan on discarding existing applications, you must assess ERP integration for each of the apps in question. This process is time-consuming. And even if you happen to be lucky, you’ll find even the best ERP falling one or two applications short in compatibility space. In this instance, opting into an ERP with an open API ensures that your developer is able to tweak the system to integrate all of your current apps.
- A lack of compliance. A majority of ERP solutions are designed for financial compliance. Thus the problem is less of a technical shortcoming and solely due to how the ERP implementations are conducted. When an accountant is not made a part of the ERP project, it’s easy to gloss over financial compliance. This is usually because the CEO or CIO is often focused on streamlining processes to drive efficiency. It is important to understand that without the auditing and regulatory knowledge of a CPA, the financial regulations can easily be overstepped. For example, GAAP requirements and Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) protocols for US-based public companies. This issue is easily resolved by including a certified accountant in your ERP project team. They can verify if the configuration, controls, and processes are compliant and make recommendations on the audit controls, where necessary.
- Potential security risk. ERPs aspire to cover operational and financial tasks. This overarching infrastructure lends to ERP its strengths. These include; shared files, integrated and automated manual processes, a central database, and a collaborative platform. They are useful as they drive efficiency and lower costs. Unfortunately, the same single architecture is its source of weakness. This is due to the wider the scope of ERP, the more access points it possesses. Meaning there are higher chances of an internal data breach occurring. Although firewalls and encryption are put in place to mitigate this risk, the fact remains all your data is still available in this system superhighway. A poorly designed ERP heightens, even more, the security risk. The risk of incompatible applications should not be ignored as they can lead to crashes. Having limited resources such as reporting tools forces users to import external files; this leads to a firewall break. Also, a disgruntled tech employee can wreak large-scale havoc, and any delayed updates or an old system version leads to exposing all your data to hacks. Fortunately, ERP vendors are fully capable of putting up security checks and controls. They take this role very seriously as any breach is a death kiss to their business.
The Latest ERP Trends

There is significant hype around Internet-of-Things and artificial intelligence, and thus, ERP trends revolve around predictable tech developments. Possibly because of the more complex setup of ERP, this niche is playing catch up to other SaaS solutions. Below is a compiled list of trends that are gaining traction among ERP vendors, be it legacy and startups:
SaaS and on-premise ERP Hybrid
ERP, due to its complexity, has a lot of grey areas in between SaaS and on-premise. Some companies will prefer a hybrid approach. It chooses to integrate cloud inventory management into its on-premise accounting-centric ERP or a cloud payroll into a local HR-focused ERP. This strategy makes sense from a cost and process perspective. And this is driving vendors, both legacy and startups, to offer hybrid ERPs. For instance, Oracle chooses not to replace its on-premise licensing, instead choosing to co-opt it with cloud solutions. Also, Salesforce, a pioneer enterprise cloud platform, offers users integration with legacy on-premise solutions such as SAP and Siebel.
Two-tier ERP
On the other hand, large multinational companies are choosing a two-tier ERP approach. In this setup, two ERP systems are implemented, and tier 1 is placed at the corporate level, while tier 2 is placed at the subsidiary level. This strategy was sought to overcome the limitations identified by big corporations when developing an overarching ERP system. which is supposed to run across a multi-country organization, replete with stark regulatory, cultural, geopolitical, and market differences.
Social ERP
Billed as ERP 2.0, the social ERP adds social media data. For instance, Twitter and Facebook profiles and posts are included in the reviewed data. Mainly the integration is a CRM initiative. Businesses will thus leverage online customer engagement, brand mentions, public data, friend networks, and likes and shares to gain tacit customer knowledge.
Mobile ERP
Currently, some ERP solutions offer native apps for iOS, Android, and Windows. A majority of these, however, are pared-down versions featuring only the most important KPIs. For instance, sales, leads, and web traffic. However, this means you can remain connected and productive remotely. Unfortunately, mobile access can be a double-edged sword. This is because the security risk is heightened when sensitive data is accessed anywhere and through a device that the company does not issue. A good mobile ERP will allow separate user permission to help you manage who can access company data through their phones.
What to do to maximize your ERP Software

ERP platforms provide businesses with the business processing tools they require to manage operations. These applications can streamline workflows, facilitate collaboration, process transactions, among other things. However, it should also be acknowledged that ERP solutions are not meant to be approached as a silver bullet that will automatically optimize your entire business. Instead, perceive it as a tool that will reinforce the work system you’ve already set for your business operations.
If you want to benefit the most from your investment, you will need to effort. You must learn how it works and understand how you can make it work for your business. The way to do this is by applying some of these best practices listed below.
- Establish key performance indicators. Before implementing an ERP system, you need to know what goals you want to achieve in your organization. You need to set concrete and clear key performance indicators. They are in place to help you guide your workflows in the desired direction and evaluate your success later.
- Have a concise workflow in mind. It is not a wise idea to go about your day-to-day operations blindly. You need to plan how exactly you want to achieve the business goals you’ve set by having a workflow in mind. Firstly, define the roles and responsibilities and come up with a proper chain of command of the personnel in your organization. After this, you need to lay out specific steps that one needs to do to finish particular projects. Lastly, you will need to be set on how you want tasks to move. This is from the moment they are made to the point at which they are accomplished. Doing so makes it easier to determine if your projects are being done correctly and help you pinpoint inefficiencies within your system.
- Create a concrete and clear timeline in mind. For every task your organization undertakes, you ought to have a specific time frame in which you expect it to be accomplished. This is helpful because it results from inaccurate estimations of project completion and helps you gauge the productivity of your team.